Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd

Arthritis is a condition where inflammation occurs in the joints. It can affect the small joints in the feet and ankles. This inflammation leads to the breakdown of articular cartilage, a slippery substance covering the joints which facilitates smooth bone movement during activities.
When this cartilage deteriorates, bones may rub against each other, causing pain, swelling, tenderness, and a reduced range of motion.
There are three main types of arthritis in the foot and ankle, which are caused by various factors:
This form is often associated with age-related wear and tear, which causes the cartilage to become frayed and rough. This results in bones rubbing together, often accompanied by the formation of bone spurs. Risk factors for this condition include obesity and genetic predisposition.
This is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the joint tissues, particularly the synovium. It leads to damage in bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons, potentially causing joint deformity.
This develops following an injury to the foot or ankle, such as fractures or dislocations, which can lead to arthritis in the affected joints.
The symptoms of arthritis in the foot and ankle vary based on the affected joint.
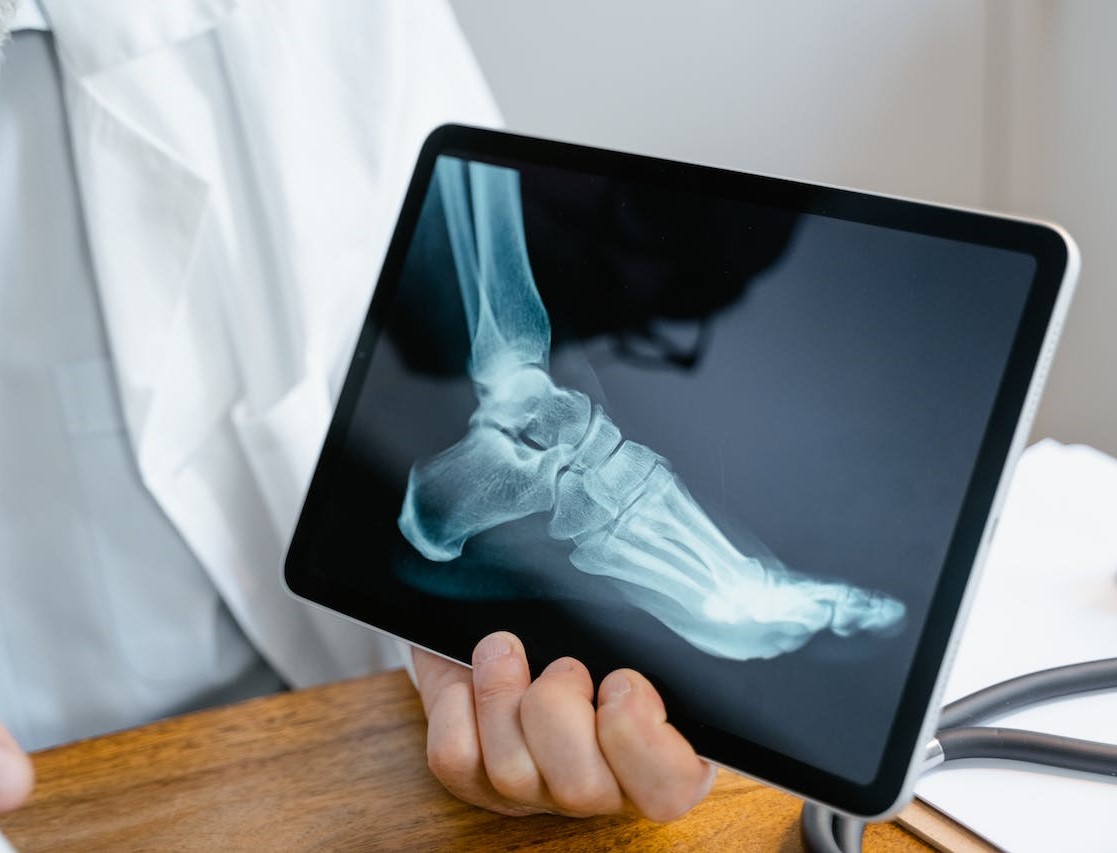
The process of diagnosing arthritis in the foot and ankle involves several steps:
There are several non-surgical treatment options available for arthritis of the foot and ankle. These treatments aim to manage symptoms, maintain mobility, and slow disease progression.
Activity Modifications |
Initially, the foot and ankle specialist may suggest modifications such as avoiding activities that worsen pain, switching from high-impact to low-impact activities, and weight loss to reduce joint stress and alleviate symptoms. |
Physical Therapy |
Tailored exercises can enhance joint flexibility and muscle strength, contributing to pain relief and improved mobility. |
Orthotics and Braces |
Shoe inserts, custom-made shoes, and braces can provide joint support, reduce pressure on the foot and ankle, and correct deformities. |
Medications |
Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers can reduce joint swelling and alleviate pain. In persistent cases, steroid medications may be injected into the joints for relief. |
When non-surgical treatments are not effective in managing the symptoms of arthritis of the foot and ankle, surgical options may be considered.
This minimally invasive surgery is useful in the early stages of arthritis. It involves using an arthroscope to view and clean the joint area, removing any foreign tissues or bone spurs.
This procedure fuses the bones together, using rods, pins, screws, or plates. The fused bones reduce pain by eliminating motion in the arthritic joint.
In this surgery, the damaged cartilage and bone are removed and replaced with artificial implants. This option is considered for patients with advanced arthritis and aims to relieve pain while offering more mobility than fusion.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
While arthritis of the foot and ankle cannot always be prevented, certain strategies can reduce the risk or delay the onset of the condition.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 18 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
While arthritis of the foot and ankle is a chronic condition that has no cure, various treatment options can help manage its symptoms. These include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, medications, and in some cases, surgery. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of further joint damage.
Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or walking can be beneficial for managing arthritis of the foot and ankle. They help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength without putting excessive stress on the joints. Consult with a foot and ankle specialist for an exercise plan suited to your condition.
Leaving arthritis of the foot and ankle untreated may lead to a progression in joint damage, increased pain, and a potential decrease in mobility and quality of life. Early management can help support joint function and reduce the risk of complications.