Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
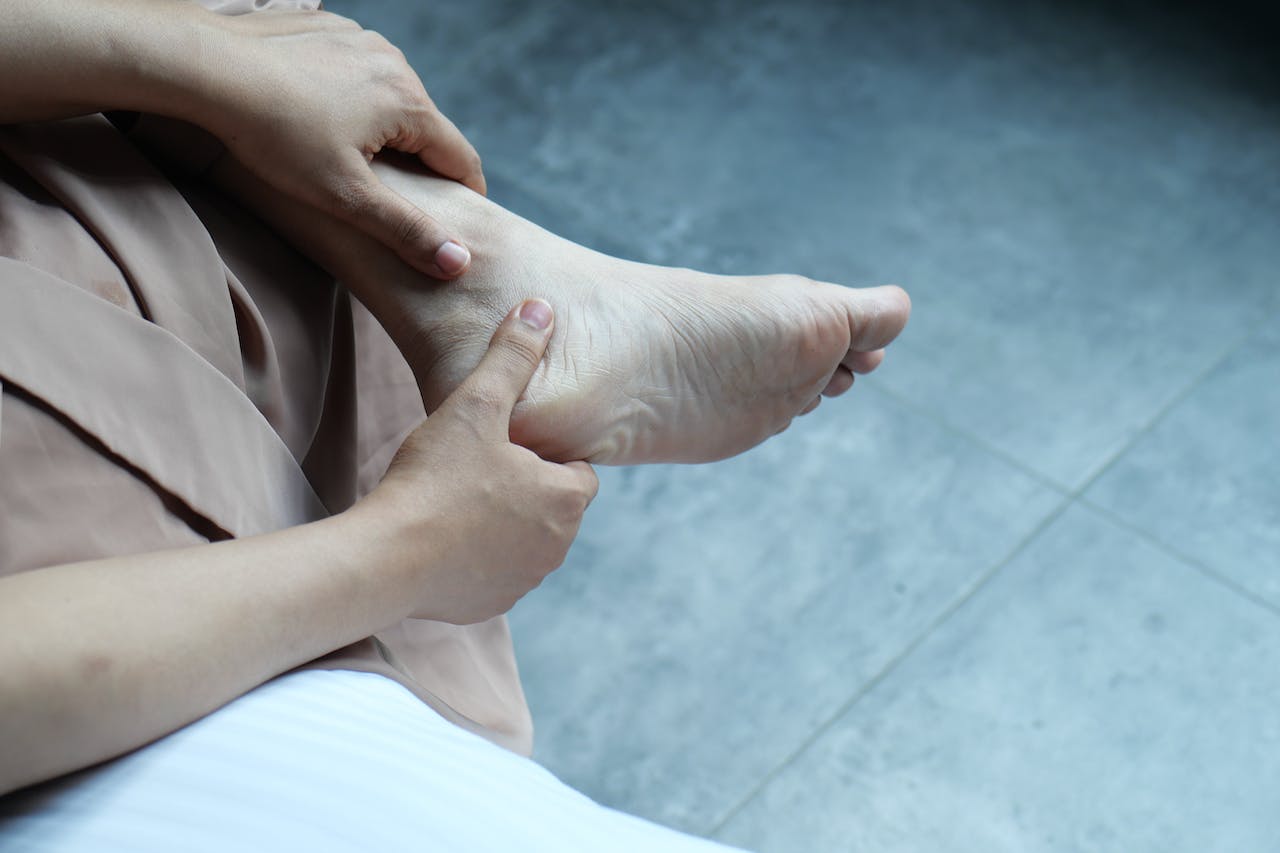

Heel pain encompasses discomfort felt in the heel area, commonly caused by excessive stress on the feet.
This condition may be indicative of chronic conditions such as plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, or heel spurs, which may limit mobility and negatively affecr daily activities.
Heel pain is often caused by repetitive stress on the feet. This can occur through activities such as playing sports on hard surfaces or wearing shoes that irritate sensitive tissues.
Common conditions causing heel pain may include:
Common indications of heel pain include:
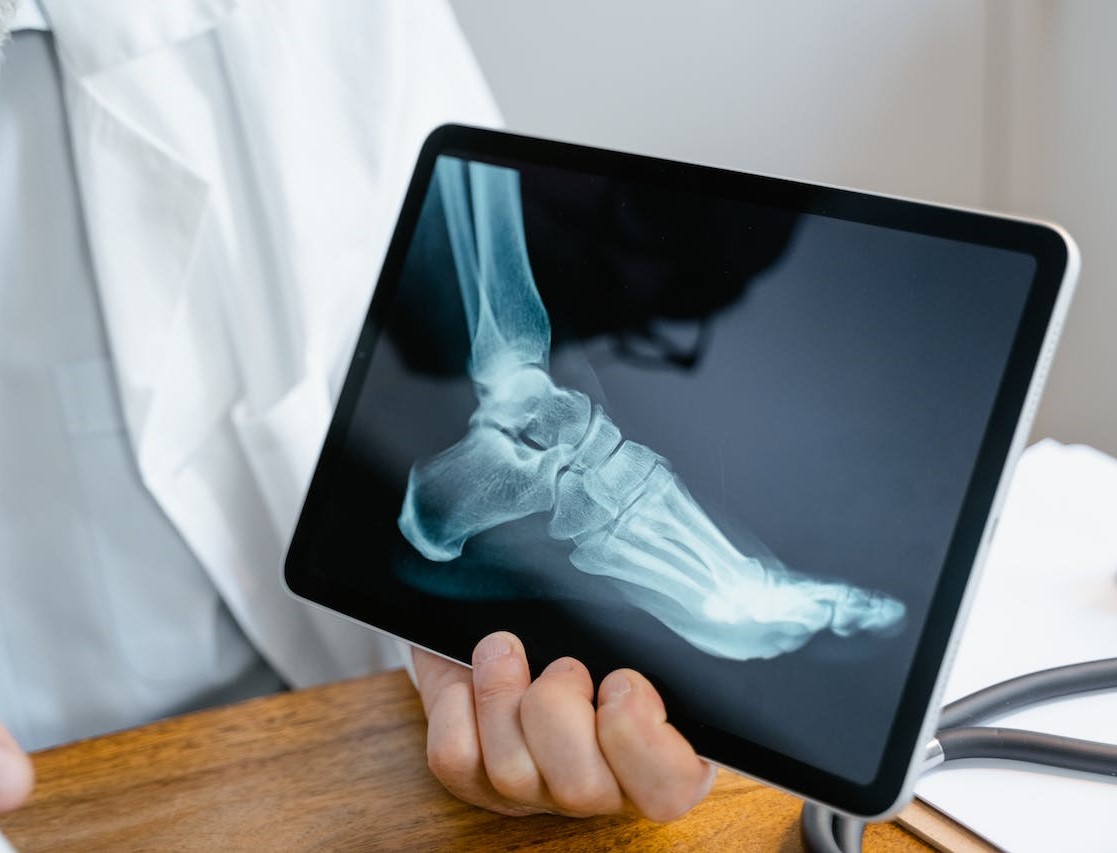
The diagnostic process for heel pain typically involves the following steps:
For most individuals, heel pain can be effectively managed with non-surgical treatments. These interventions aim to alleviate pain and inflammation while improving foot flexibility.
Rest and Ice Application |
Initially, the heel specialist may suggest resting the affected foot and applying ice to reduce swelling and alleviate pain. |
Medications |
Over-the-counter pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation. |
Orthotic Devices and Taping |
Shoe inserts, both over-the-counter and custom-made, can provide support and relieve pressure on the heel. Night splints and walking boots may be needed in more severe cases. Athletic or medical tape can also be used to support the foot arch or heel, providing relief and stability. |
Physical Therapy |
Techniques like massage, ultrasound therapy, and specific exercises can help break up soft tissue adhesions. This allows for a reduction of pain and inflammation. |
Stretching Exercises |
Regular stretching of the calf muscles and plantar fascia can improve flexibility and reduce tension in the feet, aiding in pain relief. |
While rare, certain cases of heel pain may require surgical intervention, especially if non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief.
This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia to release tension and relieve inflammation. It is typically reserved for severe cases of plantar fasciitis.
If a heel spur is causing severe pain and has not responded to other treatments, surgery may be necessary to remove the spur.
In cases where Achilles tendinitis is severe and persistent, surgical intervention may be required to repair the Achilles tendon.
If bursitis is the primary cause of heel pain, surgery to remove the inflamed bursae might be considered.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Certain measures may reduce the risk of developing heel pain.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 18 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
While it may be possible to walk with mild heel pain, this should be done in moderation to prevent straining the foot. Activities that exacerbate the pain should be limited, and the foot should be rested regularly to alleviate symptoms. If you experience persistent or increasing discomfort, consult our heel specialist for a prompt evaluation and effective management strategies.
Avoid high-impact exercises that put excessive stress on the heel, such as running, jumping, or activities on hard surfaces. Opting for low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can help maintain fitness without aggravating heel pain.
Neglecting heel pain can lead to worsening symptoms and potentially chronic conditions, affecting mobility and quality of life. Early intervention by a heel specialist can prevent complications and ensure effective treatment.
Heel pain that persists, worsens, or impacts daily activities should be evaluated by a heel specialist. Signs such as swelling, redness, or difficulty walking are indicators that medical intervention is necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment.