Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
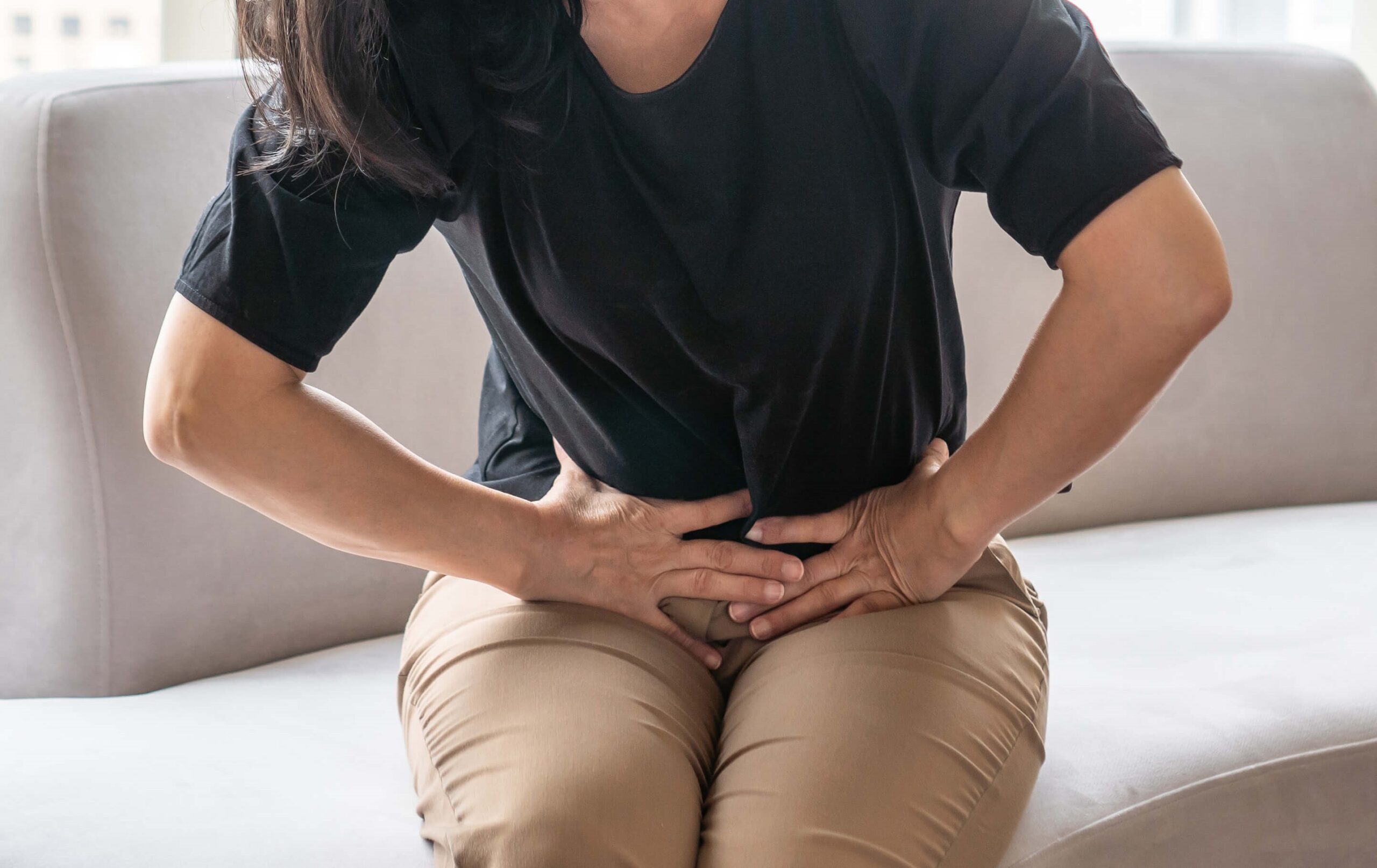

Snapping hip syndrome, also known as dancer’s hip, is a condition characterised by a snapping sound or sensation in the hip during certain movements such as walking, running, swinging the leg, or transitioning from a seated position. It primarily arises from the interaction of inflamed muscle tendons with the hip socket bone (acetabulum) or the proximal thigh bone (femur). The tension in the muscle, when released, results in the snapping sensation.
Snapping hip syndrome is not usually a cause for alarm and often remains painless. In certain situations it can escalate to pain and inflammation, potentially impacting overall performance and activity levels.
The causes of snapping hip syndrome can be traced to several factors:
The primary symptom is an audible snapping or clicking sound, or a feeling of popping in the hip during movement. Initially, this symptom often occurs without associated pain. With time, the snapping may lead to a dull ache or pain in the hip, particularly during or after movement.
Other symptoms that accompany this can include:
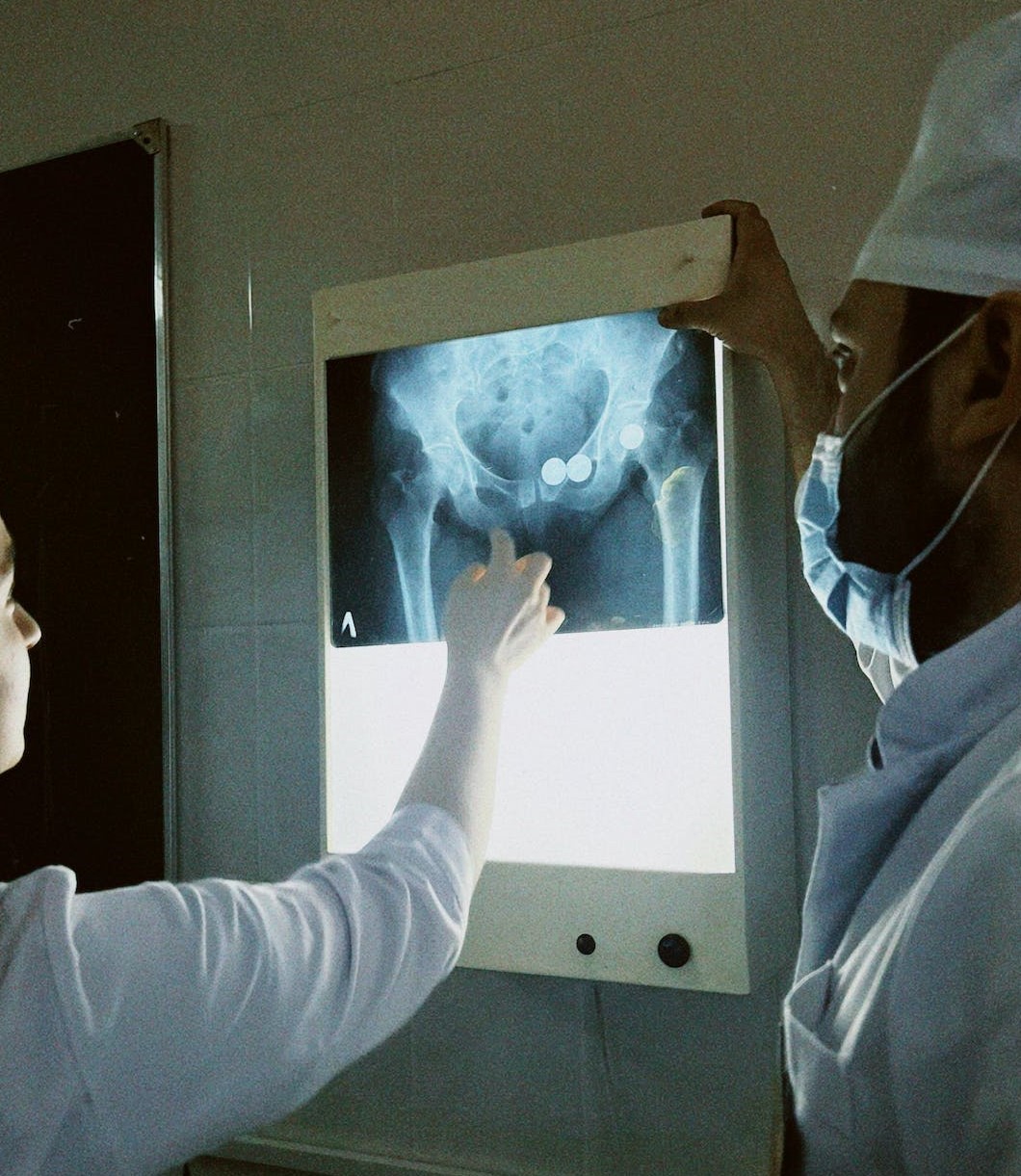
The process of diagnosing snapping hip syndrome involves several steps:
Several non-surgical treatment options can be used to manage snapping hip syndrome. These aim to alleviate symptoms and improve hip function without the need for surgical intervention.
Activity Modification and Rest |
Initially, hip specialists may suggest reducing the level of physical activity and resting the affected hip to allow healing of the muscles and tendons. This is often the first line of treatment for less severe cases. |
Pain Relief and Anti-inflammatory Medication |
Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation. |
Physical Therapy |
The hip specialist may suggest engaging in physical therapy to stretch the tightened muscles and improve the range of motion in the hip. This includes specific exercises to target the affected areas. |
Steroid Injections |
In cases where the snapping is persistent and associated with pain, steroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. |
When non-surgical treatments are not effective in managing snapping hip syndrome, surgical interventions may be considered.
This keyhole procedure is primarily used to address issues within the hip joint. During hip arthroscopy, a small camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the hip joint to guide the hip surgeon in repairing a labral tear or removing loose bodies within the joint. The minimally invasive nature of this procedure involves smaller incisions, which greatly reduces recovery time compared to traditional surgical methods.
In cases where tight muscles are the primary cause of the snapping hip, endoscopy may be performed. This procedure involves the use of an endoscope to release tight muscles and remove inflamed tissue surrounding the hip joint. Like arthroscopy, endoscopy is minimally invasive and aims to alleviate the tension causing the snapping sensation.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
While it may not be possible to prevent snapping hip syndrome entirely, several strategies can reduce the risk of developing the condition.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 18 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
While snapping hip is generally not a severe condition, it can occasionally signal underlying issues such as a labral tear or hip impingement. These conditions, if left untreated, may lead to complications like osteoarthritis, chronic pain, or reduced mobility. Consult with our hip specialist if you experience persistent pain or discomfort, especially when accompanied by a snapping sound.
The duration of snapping hip syndrome varies depending on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of treatment. In some individuals, the condition may resolve with conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, or medication. Persistent cases might require a more extended period of treatment or even surgical intervention for resolution. Reach out to us for personalised care and tailored management techniques, for prompt treatment and effective recovery.
Specific exercises can help alleviate symptoms of snapping hip syndrome. These include hip flexor stretches, iliotibial band stretches, strengthening exercises for hip abductors and adductors, and core stability workouts. Perform these exercises under the guidance of a hip specialist to ensure they are done correctly and effectively.
Walking with snapping hip syndrome is possible, although some individuals may experience discomfort or pain. Modifying activities and using pain relief strategies can help manage symptoms during walking. If walking becomes increasingly painful, consult our hip specialist for an appropriate treatment plan.
Surgical interventions for snapping hip, such as hip arthroscopy or endoscopy, are typically performed using minimally invasive techniques, which tend to result in less postoperative pain compared to traditional open surgeries. Pain management and rehabilitation post-surgery can also ensure the patient’s comfort and recovery.