Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
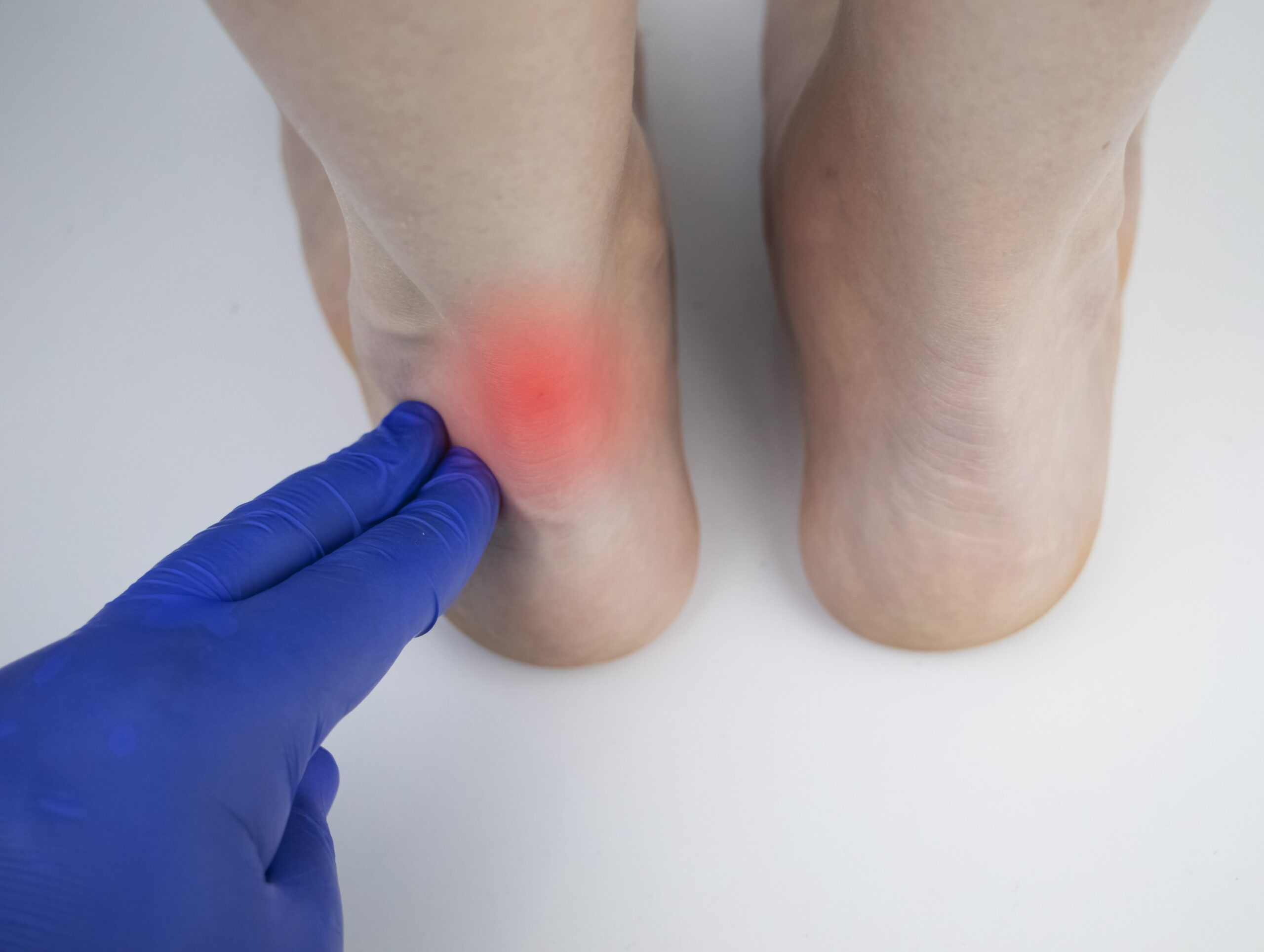
Achilles tendinitis is a condition characterised by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the large tendon at the back of the lower leg. This tendon plays a role in movement, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. It facilitates activities such as walking, running, climbing stairs, jumping, and standing on tiptoes.
While the Achilles tendon is capable of enduring stress, overuse and degeneration make it susceptible to tendinitis.
Achilles tendinitis manifests primarily in two different forms:
This occurs when the fibres in the mid-portion of the tendon experience degeneration, leading to small tears, swelling, and thickening of the tendon.
This form involves inflammation and damage to the tendon fibres near their attachment to the heel bone. This can be accompanied by the development of bone spurs.
Achilles tendinitis is usually caused by repetitive stress on the tendon. Several factors can influence this:
Achilles tendinitis presents a range of symptoms and signs that can vary in intensity.
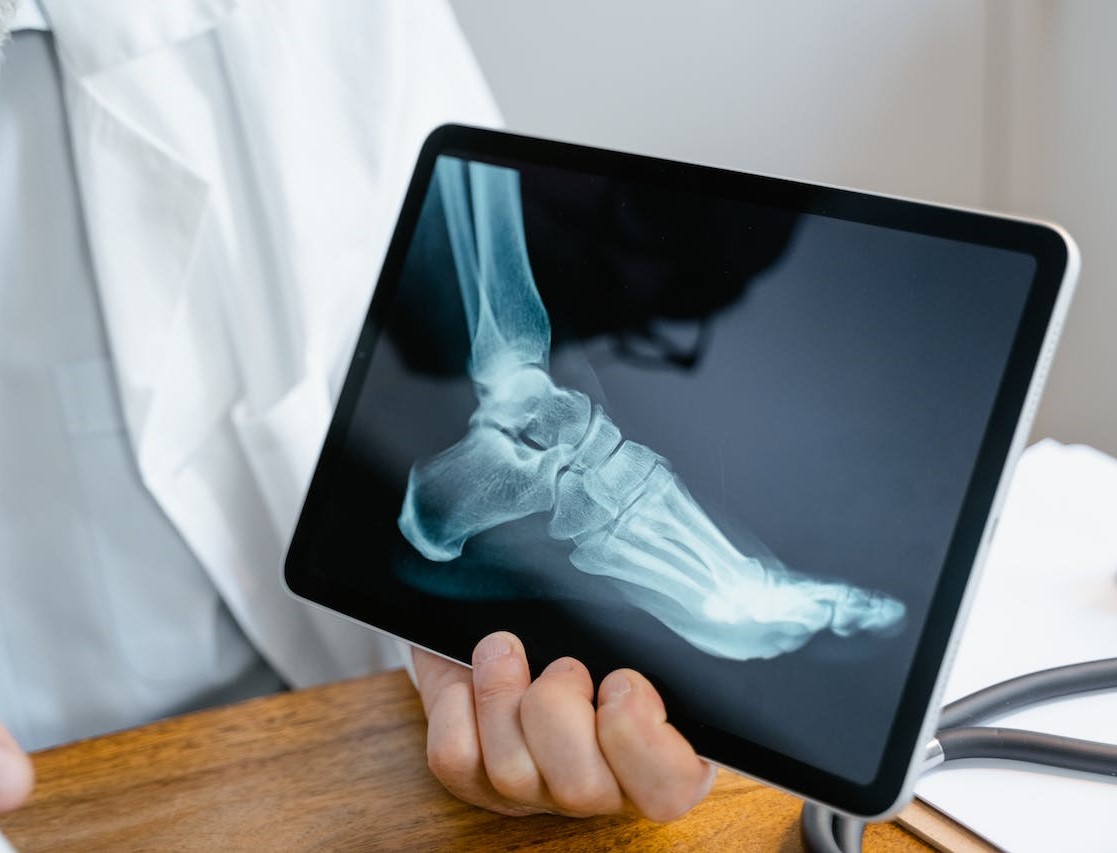
The diagnosis process for Achilles tendinitis encompasses clinical evaluation and various diagnostic tools.
Achilles tendinitis is primarily treated using non-surgical methods, used to alleviate symptoms and stimulate healing.
Rest and Ice |
Initially, the Achilles tendon specialist may suggest reducing or temporarily stopping activities that aggravate the tendon. Applying ice can also help manage pain and reduce swelling. |
Medications |
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can alleviate pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, stronger medications may be prescribed. |
Physical Therapy |
This includes specific stretching and strengthening exercises to facilitate healing and fortify the Achilles tendon and its supporting structures. This may include eccentric strengthening exercises to load or stretch the tendon. |
Orthotic Devices |
Shoe inserts or wedges that slightly elevate the heel can relieve strain on the tendon and provide cushioning, reducing the force exerted on the Achilles tendon. |
Shockwave Therapy |
This method uses low or high-energy shockwaves applied to the Achilles tendon to help stimulate healing. |
If the Achilles tendinitis does not improve after 6 months of non-surgical treatments, surgical intervention may be considered.
This surgery focuses on lengthening the calf muscles (specifically the gastrocnemius muscle) to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon. It can be beneficial for patients whose tendon strain is exacerbated by tight calf muscles.
In this procedure, the surgeon removes the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. If there is extensive damage to the tendon, debridement might also involve tendon repair.
This procedure is necessary when there are severe tears in the Achilles tendon. The surgeon works to repair and reattach the torn sections of the tendon.
If the Achilles tendon is severely damaged, a tendon transfer might be considered. In this surgery, a less important tendon from the foot is used to replace the damaged Achilles tendon.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Preventative measures can help reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendinitis.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
If Achilles tendinitis is not addressed, the condition may worsen, potentially leading to increased pain, swelling, and limited mobility. In some cases, ongoing inflammation and stress on the tendon can result in an Achilles tendon rupture, a more severe injury requiring surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment are recommended to address these concerns.
The healing time for Achilles tendinitis varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment. Generally, with appropriate non-surgical treatments like rest, physical therapy, and proper footwear, patients may see improvement within a few weeks to several months. Consult an Achilles tendon specialist for a personalised treatment plan and accurate prognosis.
Specific stretching and strengthening exercises can aid in the treatment of Achilles tendinitis. These include calf stretches, eccentric heel drops, and exercises to strengthen the lower leg muscles. These exercises should be performed under the guidance of an Achilles tendon specialist to ensure they are done correctly and effectively.
While moderate physical activity may be possible with Achilles tendinitis, adjust the type and intensity of exercise to avoid aggravating the condition. Low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling are typically more suitable. An Achilles tendon specialist can guide you through safe exercises and suggest appropriate activity modifications suited to your specific condition.