Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
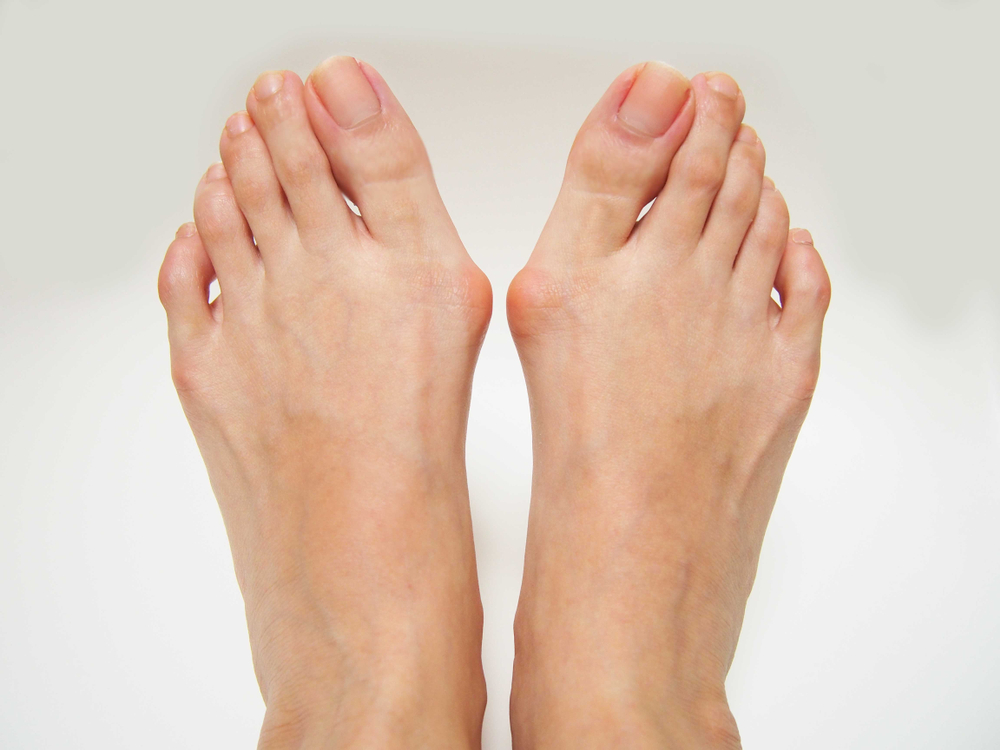
Bunions, also known as hallux valgus, are a common foot condition characterised by a noticeable bony bump at the base of the big toe. This condition develops over time due to alterations in the structure of the bones at the front part of the foot. These changes cause the big toe to move towards the second toe, which results in the protrusion of the joint at the base of the big toe. This forms the bunion bump.
The formation of a bunion is a progressive process, during which the normal structure of the bone is altered. As this deformity increases, it can cause discomfort and pain, making it challenging to wear shoes or walk. Bunions can vary in size, and in some cases, smaller bunions, referred to as bunionettes, may develop on the joint of the little toe.
Bunions are caused by a mix of genetic, environmental, and biomechanical factors.
Bunions present a range of symptoms and signs, which typically develop progressively.
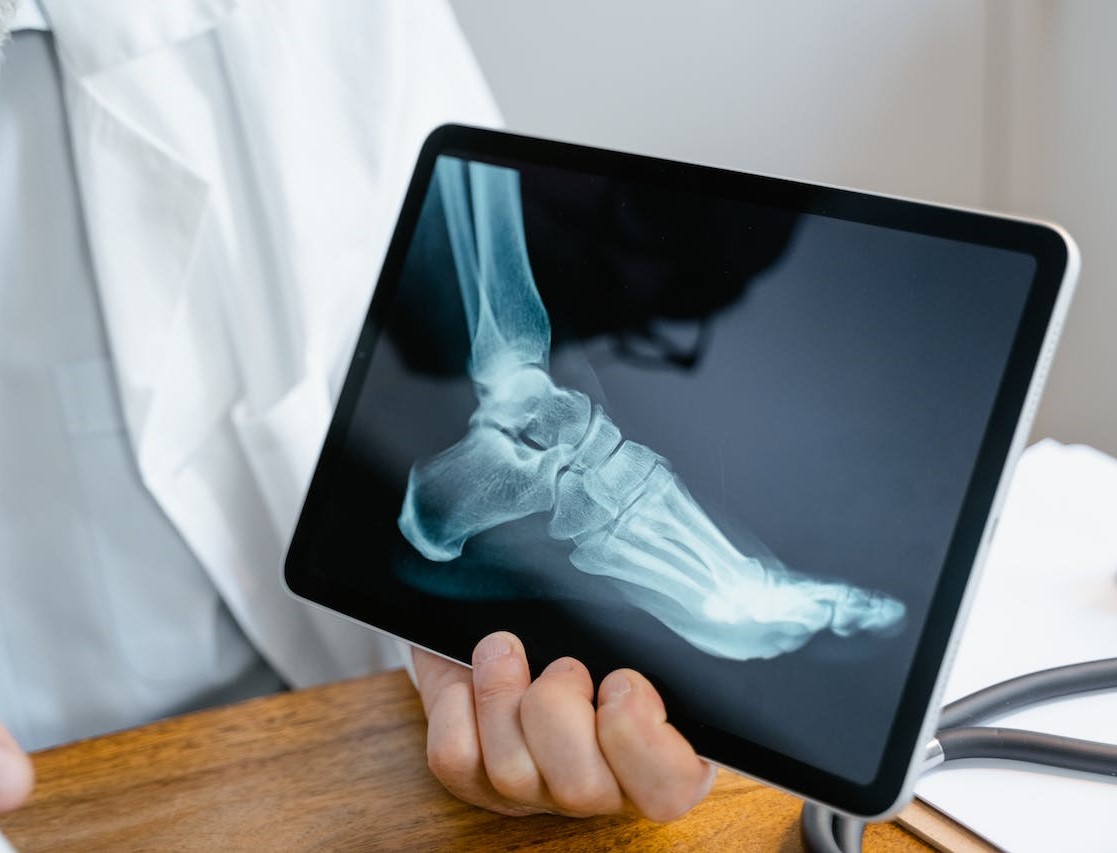
The diagnosis of bunions involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging.
Bunions can initially be managed by non-surgical treatments, which aim to alleviate pain and prevent further progression of the condition.
Footwear Modifications |
In less severe cases, the foot specialist may suggest modifying footwear to provide pain relief. Shoes should be comfortable, with a wide toe box to accommodate the bunion and prevent crowding of the toes. Custom or over-the-counter orthotic devices can also be beneficial, to help redistribute pressure and align the foot properly. |
Padding and Cushions |
Over-the-counter bunion pads or cushions can provide a buffer between the foot and the shoe, reducing pain and discomfort. These pads help in distributing pressure more evenly across the foot. |
Medications for Pain Relief |
Pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can be used to manage pain and inflammation associated with bunions. In some cases, cortisone injections may also be considered. |
Physical Therapy |
Engaging in physical therapy can help maintain joint flexibility and strengthen the muscles around the foot and big toe. Exercise and stretches can be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving foot function. |
When non-surgical treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be considered to correct the bunion and alleviate pain. The choice of surgery depends on the severity and nature of the bunion.
This surgery involves removing the swollen tissue from around the big toe joint. It can be used to alleviate the pressure and discomfort caused by the bunion.
This is a common surgical approach used to realign the bones in the foot. It may involve removing a portion of the bone to straighten the big toe and correcting the abnormal angle in the big toe joint.
For more severe bunions, joint fusion might be necessary. This procedure involves removing damaged cartilage and bone, and then fusing the bones of the joint. While this can eliminate the source of pain, it can result in permanent immobility of the joint.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Preventing the development or worsening of bunions involves several practical measures focused on foot health and care.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Exercises and stretches that strengthen the muscles of the feet and toes can be beneficial for individuals with bunions. These exercises include toe curls, towel scrunches, and picking up objects with the toes. Stretching exercises that enhance toe flexibility can also help in alleviating discomfort. For tailored exercise plans and guidance, consult with your foot specialist.
Walking barefoot, particularly on natural, soft surfaces, allows the feet to move naturally without the constraints of shoes. It can help in strengthening the foot muscles and improving balance. This should be approached with caution and at the discretion of your foot specialist.
If a bunion is left untreated, it may lead to further foot deformities and complications such as bursitis, hammertoe, or metatarsalgia. These complications can result in increased pain and mobility issues. Early consultation with a foot specialist can help manage the condition effectively and prevent further progression.
Bunions and gout can present with similar symptoms, such as pain and swelling in the big toe. A bunion is a structural deformity, while gout is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint. Consult your foot specialist for a definitive diagnosis of your specific condition.
The treatment duration for a bunion varies depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment approach. Non-surgical treatments can provide immediate relief but may require ongoing management. Surgical treatments may offer a more permanent solution, but recovery can take weeks to months.