Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd

Bicep tendinitis is a condition characterised by inflammation or irritation of the upper biceps tendon, a structure connecting the biceps muscle to the bone in the shoulder socket. It leads to pain and weakness in the front of the shoulder.
The biceps muscle, located in the front of the upper arm, plays a role in lifting, bending the elbow, and reaching overhead. Bicep tendinitis often arises from repeated physical activities involving the shoulder, leading to overuse and strain of the tendon.
Understanding the causes of bicep tendinitis can aid prevention and treatment. Factors leading to this condition include:
The symptoms of bicep tendinitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common indicators include:
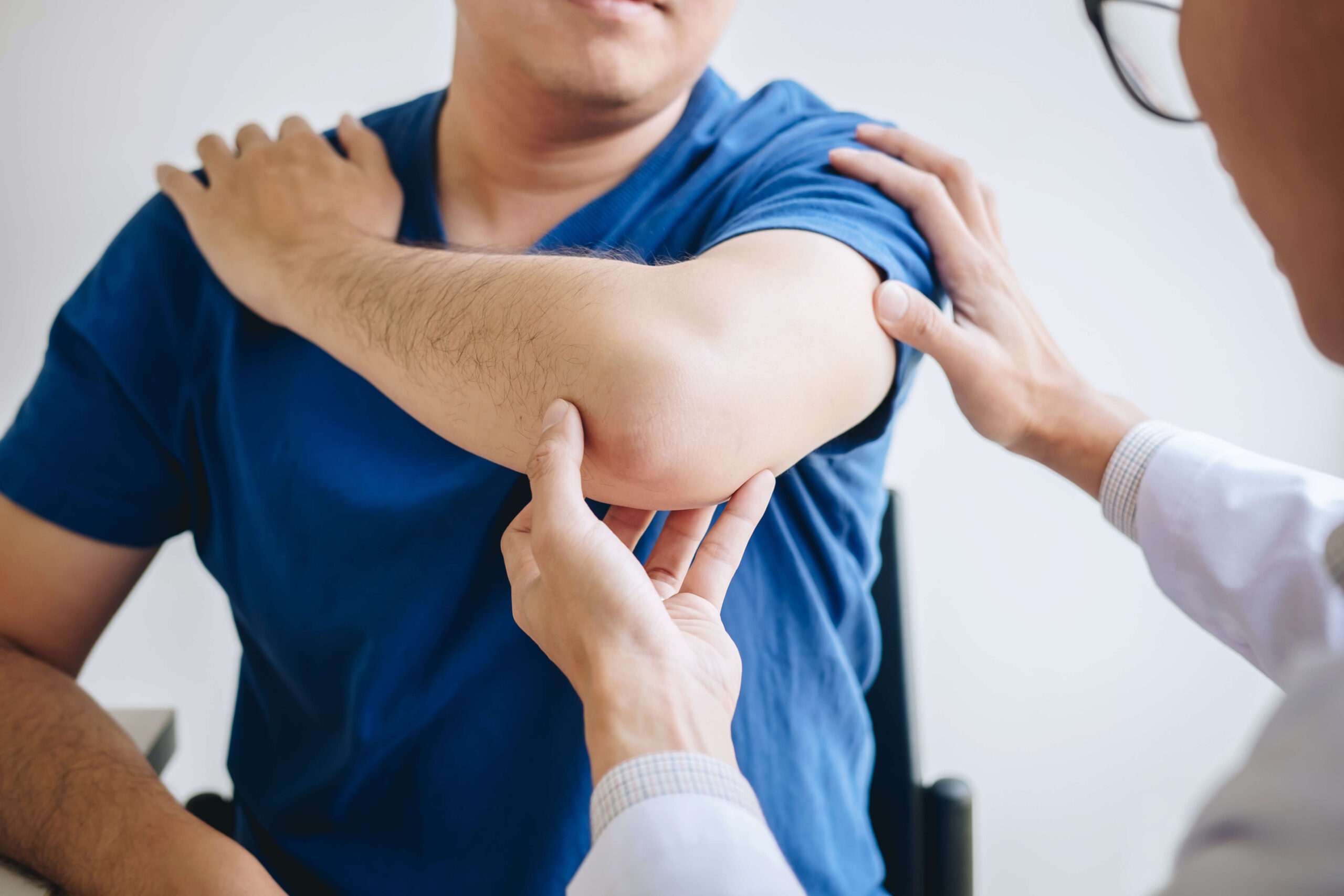
Diagnosing bicep tendinitis involves an assessment of medical history and a physical examination of the shoulder. The doctor may perform specific tests to evaluate the shoulder for related issues such as labrum tears, rotator cuff problems, or impingement.
Imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis. X-rays, while primarily showing bone structures, can reveal signs like bone spurs that may impact the tendon. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another effective tool for detailed visualisation of the biceps tendon and surrounding structures.
The initial approach to treating bicep tendinitis is usually non-surgical, focusing on relieving symptoms and promoting healing.
Rest and Ice |
The initial step in treating bicep tendinitis involves avoiding activities that exacerbate pain. Applying cold packs for 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce swelling and pain. |
Medications |
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen are used to alleviate pain and inflammation. Use these with caution, as there is a potential for side effects such as stomach, kidney, or liver issues. Topical creams containing pain relievers are also an option for localised relief without systemic side effects. |
Steroid Injections |
Cortisone, a potent steroid, can be injected around the tendon to ease tendinitis pain. Repeated steroid shots can weaken a tendon and are not ideal for tendinitis lasting more than three months. |
Physical Therapy |
Targeted exercises, including eccentric strengthening, help strengthen the muscles and tendons. Eccentric strengthening emphasises contraction of a muscle while it’s lengthening, proving effective in chronic tendon conditions. |
Platelet-rich Plasma |
This treatment involves using the patient’s blood, separating platelets and healing factors, and injecting them into the area of chronic tendon irritation. |
Dry Needling |
Performed with ultrasound guidance, this procedure involves making small holes in the tendon with a fine needle to stimulate healing factors. |
Surgery for bicep tendinitis is considered when non-surgical treatments do not provide relief or in cases with associated complex shoulder problems.
This surgery treats biceps tendon tears and SLAP tears (tears in the labrum). The procedure involves detaching the biceps tendon from the labrum and reattaching it to the upper arm bone (humerus).
The technique includes making an incision at the top of the biceps tendon, releasing it from the labrum, drilling a hole in the upper arm bone, and securing the tendon in the bone using a suture anchor.
As an alternative to tenodesis, in a tenotomy, the biceps tendon is cut away from the labrum but not reattached to the upper arm bone. This procedure is less invasive but may lead to a prominent bulge in the arm, known as Popeye syndrome.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Preventing bicep tendinitis involves strategies to reduce stress on the shoulder and biceps tendon.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Bicep tendinitis is inflammation or irritation of the upper biceps tendon, characterized by pain and weakness in the front of the shoulder.
It’s commonly caused by repetitive shoulder motions, ageing-related wear and tear, direct injuries, and associated shoulder conditions like rotator cuff tears.
Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests like X-rays and MRI.
Treatment includes rest, ice, medications, steroid injections, physical therapy, and in more severe cases, surgical interventions like biceps tenodesis or tenotomy.
Yes, through proper exercise, technique, adequate rest, ergonomic adjustments, and listening to your body to address early signs of discomfort.