Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
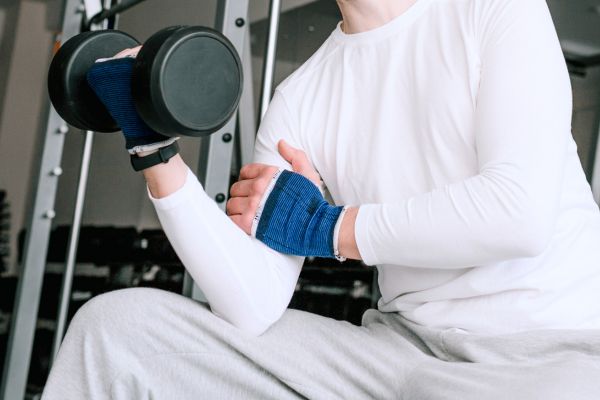

Distal bicep tears occur when the tendon attaching the biceps muscle to the elbow is damaged. The biceps muscle, located in the front of the upper arm, is connected to the shoulder and elbow by tendons, which are strong fibrous tissues. When this gets torn, it is known as a distal bicep tear.
Once torn, the biceps tendon at the elbow will not naturally reattach to the bone, impacting certain elbow movements, such as forearm supination (the action of rotating the forearm to turn the palm upwards).
Distal bicep tears can be categorised into two main types:
These involve damage to the soft tissues of the tendon but do not completely sever it from the bone. Despite the partial nature of these tears, they can still impact the function of the biceps muscle and the forearm.
This type represents a full detachment of the tendon from its attachment point at the bone. In complete tears, the entire muscle is detached, often recoiling towards the shoulder. This results in more pronounced functional deficits, especially in forearm rotation and elbow flexion.
Distal bicep tears are typically caused by a combination of factors:
The symptoms and signs of a distal bicep tear include:
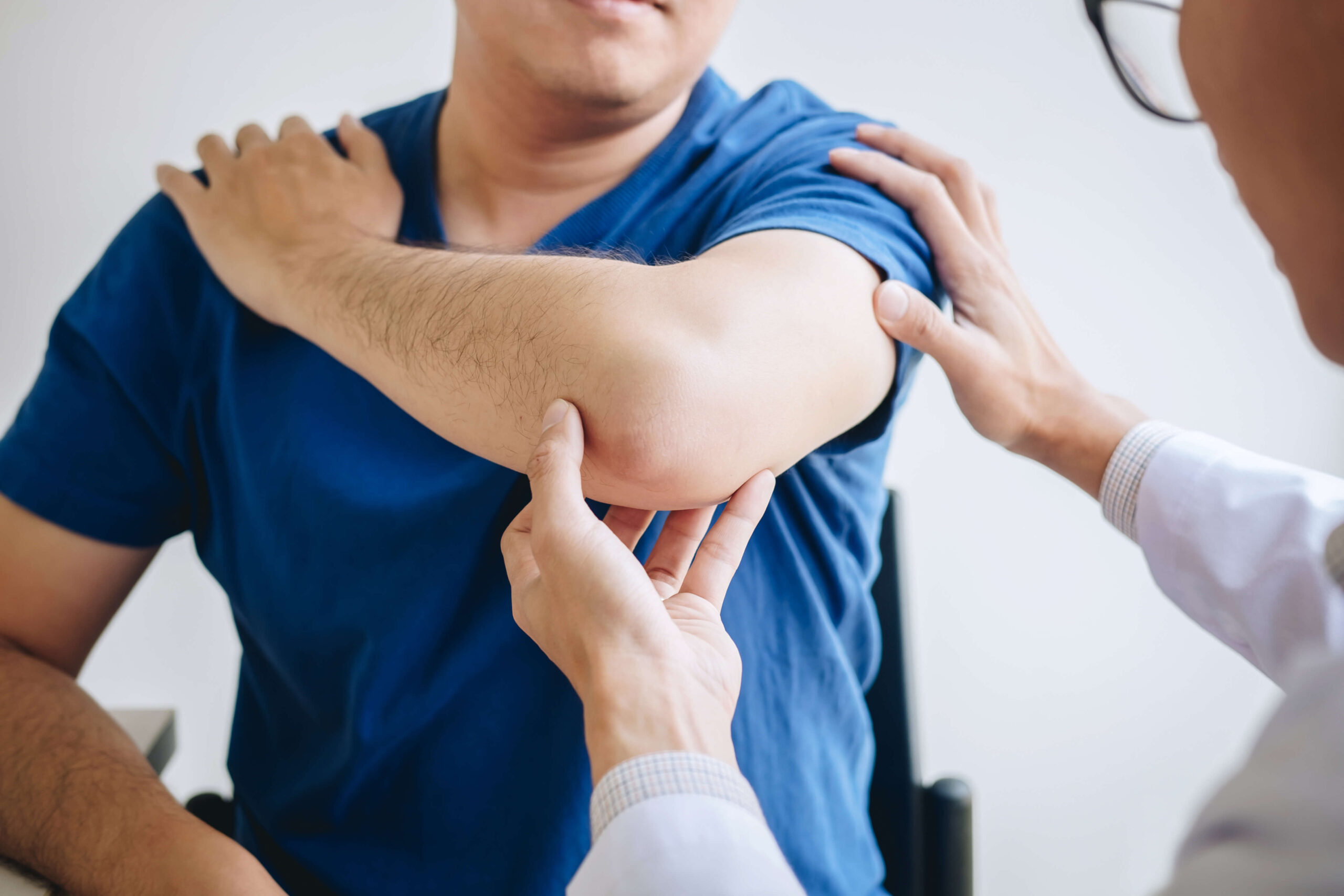
Diagnosis of distal bicep tears involves several steps:
There are several non-surgical management strategies for distal bicep tears. While they can help alleviate pain and maintain arm function, they do not facilitate the healing of the torn biceps tendon and some level of supination weakness may persist. These treatment options are typically considered for individuals who are older, less active or have medical conditions that increase the risks associated with surgery.
Rest and Activity Modification |
For less severe cases, the elbow specialist may initially suggest avoiding activities that exacerbate the injury, particularly those involving heavy lifting or intensive use of the arm. |
Medications |
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen help reduce pain and swelling. |
Physical Therapy |
This helps maintain the range of motion and strengthen the surrounding muscles in the elbow. It can compensate for the weakness caused by the torn biceps tendon. |
Surgical intervention can help restore full strength and function to the arm, especially in cases of complete tears.
This surgery aims to repair and reattach the torn tendon back to the bone. In this procedure, the tendon can be reattached using suture anchors, which are small metal implants, or through bone tunnels, where stitches are passed through holes drilled in the radius bone.
Ideally, surgery should be performed within 4 weeks after injury. Delaying surgery may lead to scarring and shortening of the muscle, complicating the repair process.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Preventive measures for distal bicep tears focus on minimising the risk of tendon injuries and supporting tendon health.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
While arm movement is possible with a distal bicep tear, the range and strength of motion may be limited. Consult an elbow specialist for a personalised treatment plan to manage the condition while maintaining arm function.
Leaving a distal bicep tear untreated can lead to persistent weakness, especially in forearm twisting motions. You may consult our elbow specialist for a tailored treatment plan to prevent long-term functional limitations.
The healing time for a distal bicep tendon varies depending on the severity of the tear and the chosen treatment method. Surgical repair generally offers a more predictable and quicker recovery timeline.
Specific exercises can aid in the recovery from a distal bicep tear. These exercises focus on strengthening surrounding muscles and maintaining range of motion. Our elbow specialist can guide you through appropriate and safe exercise routines.
With appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, returning to sports or weightlifting is possible after a distal bicep tear. The timeline and extent of return depend on the injury’s severity and the success of the treatment.