Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd

Elbow arthritis is a condition where the cartilage surface of the elbow becomes worn out or damaged. The elbow, a hinge joint comprising the humerus, ulna, and radius, relies on its cartilage for smooth movement and function. As the cartilage degrades, the bones in the elbow joint may start rubbing against each other, leading to symptoms such as pain, stiffness, swelling, and a limited range of motion.
Elbow arthritis, while not curable, can be managed effectively through various treatment options designed to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Elbow arthritis can develop due to various factors, each contributing to the wear and tear of the joint’s cartilage.
The symptoms and signs of elbow arthritis can vary, but commonly include:
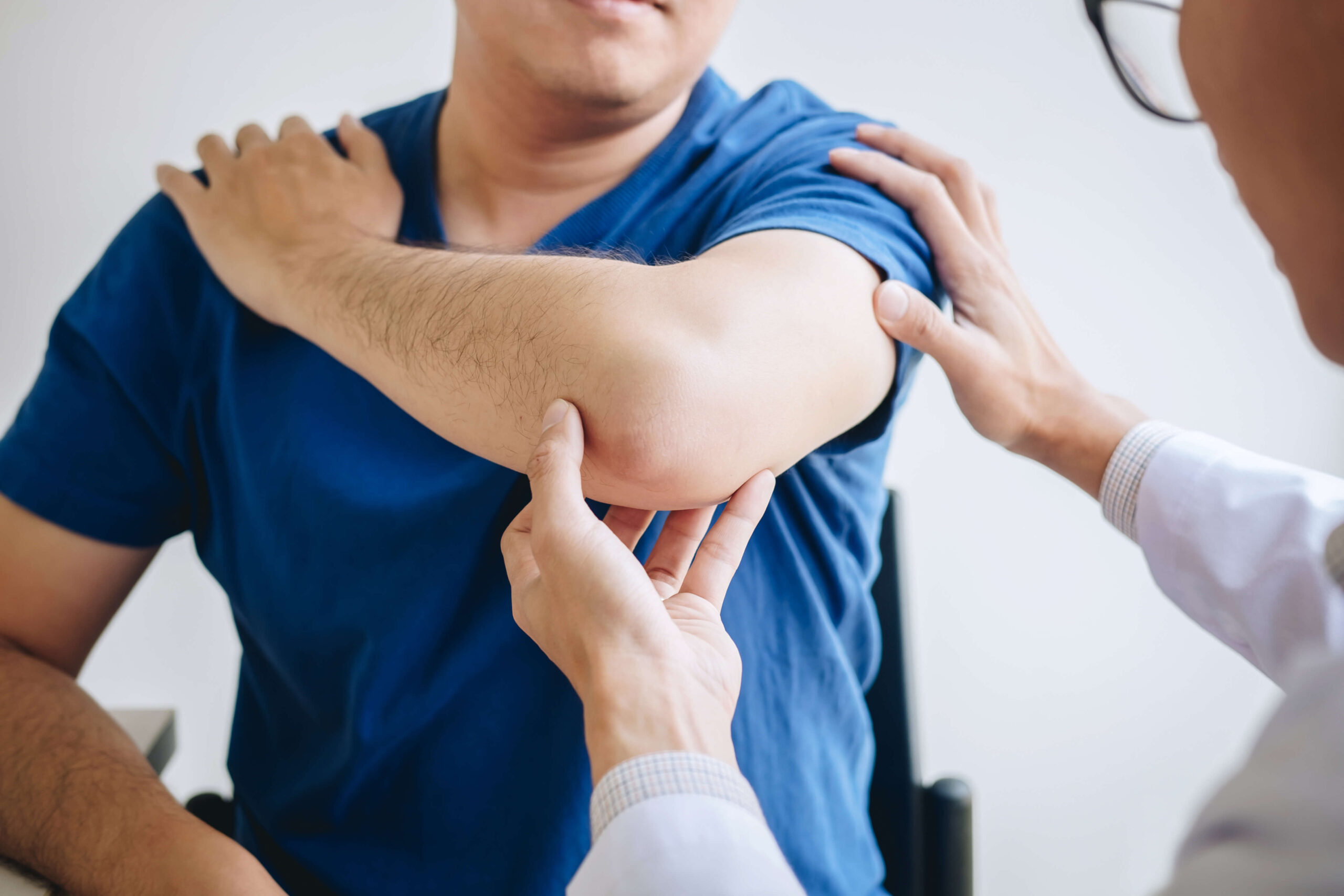
The diagnosis of elbow arthritis typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and imaging studies.
For individuals diagnosed with elbow arthritis, especially in its early stages, non-surgical treatment options are often considered. These options focus on managing symptoms and improving joint function.
Activity Modification |
For less severe cases, the elbow specialist may suggest modifying daily activities to avoid movements that exacerbate pain or put undue stress on the elbow joint. |
Medications |
Oral pain and anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce discomfort and swelling associated with elbow arthritis. |
Physical Therapy |
Engaging in physical therapy helps in maintaining or improving the range of motion and strengthening the muscles around the elbow. This helps to stabilise the joint and reduce symptoms. |
Corticosteroid Injections |
In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used to alleviate symptoms. These injections can provide temporary relief, allowing for improved joint function until further treatment is required. |
When non-surgical interventions are insufficient in managing the symptoms of elbow arthritis, surgical options may be considered.
For early-stage arthritis, arthroscopic surgery can be an option. This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions around the elbow to remove inflamed tissue, unstable cartilage fragments, or bone spurs, and to smooth out irregular joint surfaces.
In advanced elbow arthritis where the joint surface has severely deteriorated, total elbow replacement may be required. This procedure involves removing the damaged cartilage and bone and replacing them with an artificial joint (prosthesis), restoring elbow function.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
While it is not always possible to prevent elbow arthritis, some strategies can reduce the risk and mitigate the progression of the condition.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Those with elbow arthritis can generally continue using their arm given they do not engage in activities that exacerbate the pain. Gentle exercises and movements can be beneficial for those with the condition to help maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
If left untreated, elbow arthritis may progressively worsen, potentially leading to increased pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Timely consultation with an elbow specialist can help guide effective management strategies to control symptoms and slow disease progression.
Certain exercises can help maintain or improve joint flexibility and strengthen the muscles around the elbow. These exercises involve gentle stretching and strengthening, to avoid overstraining the joint. Patients with elbow arthritis can consult an elbow specialist to help determine the most suitable exercise regimen.