Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
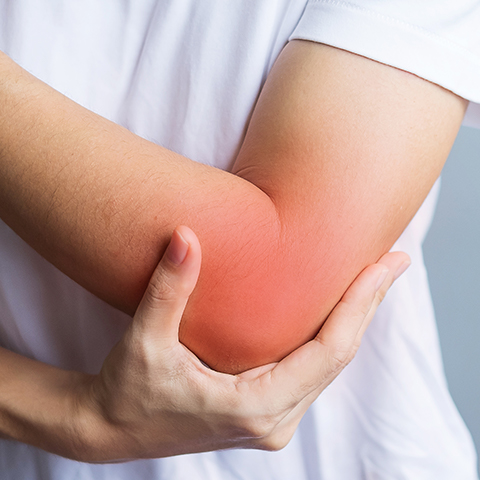
Elbow bursitis, medically known as olecranon bursitis, is a condition characterised by painful swelling at the elbow joint. This inflammation occurs in the olecranon bursa, a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues in the joint. The primary function of this bursa is to facilitate smooth movement, reducing friction between the bone and surrounding soft tissue.
In elbow bursitis, the olecranon bursa becomes irritated or inflamed, leading to an accumulation of fluid. This can result in discomfort and impaired movement of the elbow. The pain experienced can be either sudden or gradual, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the inflammation.
Elbow bursitis can arise from a variety of factors, each contributing to the irritation and inflammation of the olecranon bursa.
Common symptoms and signs of elbow bursitis include:
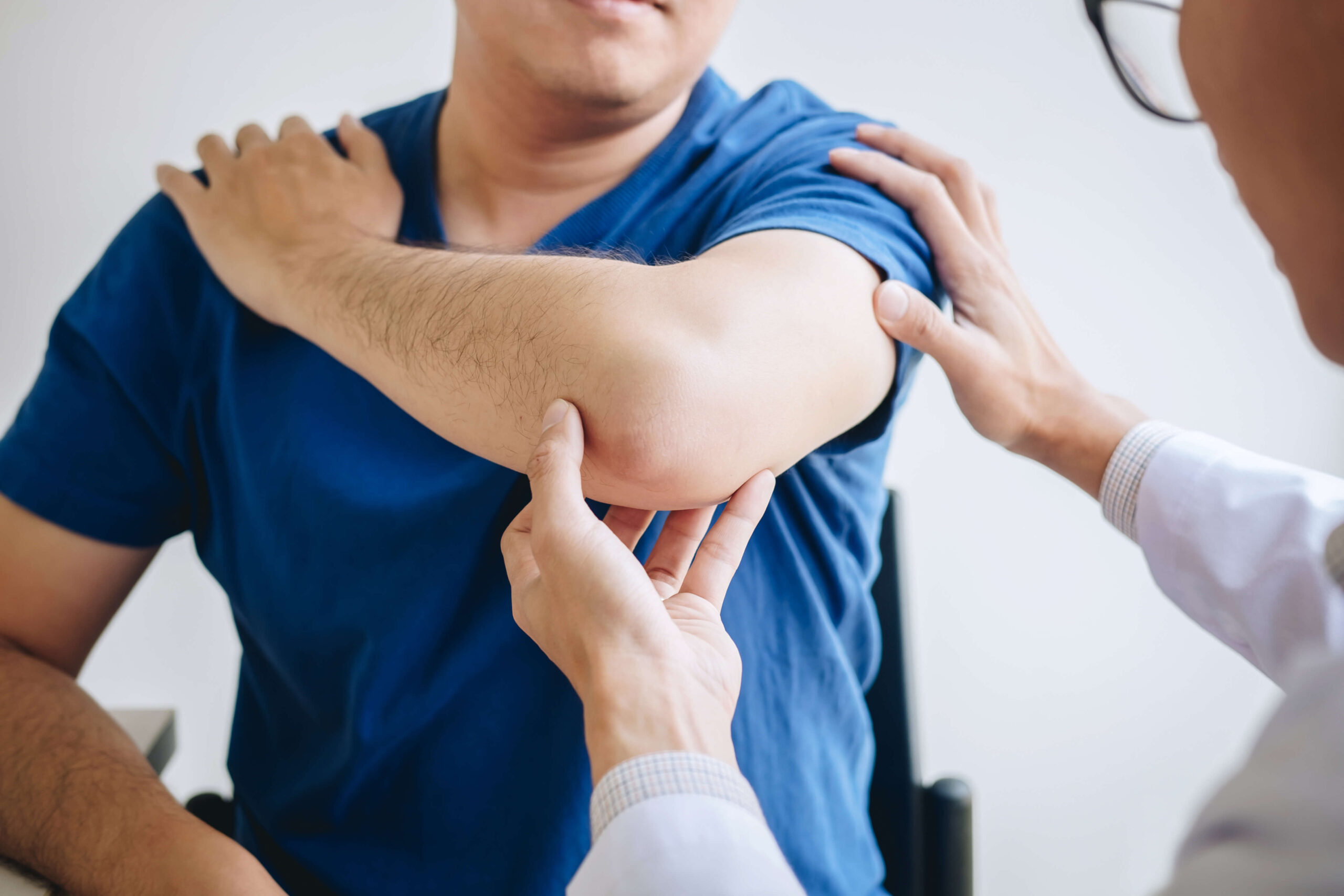
The process of diagnosing elbow bursitis typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests.
Elbow bursitis is typically treated using various non-surgical methods. These approaches are usually effective in managing the symptoms of elbow bursitis and promoting healing.
Rest and Activity Modification |
In less severe cases, the elbow specialist may suggest avoiding or modifying activities that exacerbate elbow bursitis. Rest helps in reducing inflammation and gives the bursa time to heal. |
Elbow Pads |
Elbow pads can be used to cushion the joint and protect it from further trauma or pressure, especially in situations where prolonged elbow contact is unavoidable. |
Physical Therapy |
Engaging in physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strengthen the muscles around the elbow. This can aid in recovery and help prevent future episodes. |
Medications |
Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. |
Aspiration |
In cases of severe swelling, aspiration may be conducted to drain the fluid from the bursa. While this may offer relief, it also has a risk of bursitis recurrence. |
Surgery for elbow bursitis is considered when non-surgical treatments do not provide adequate relief or in cases of severe or recurrent bursitis.
The most common surgical procedure for elbow bursitis involves removing the inflamed bursa. This procedure, known as bursectomy, is typically performed as an outpatient surgery, meaning patients can go home the same day.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Several measures can be taken to minimise stress and strain on the elbow joint, reducing the risk of developing elbow bursitis.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
While mild cases of elbow bursitis may show improvement with self-care measures such as rest, ice application, and avoiding activities that aggravate the condition, it is beneficial to consult an elbow specialist to prevent the condition from worsening. Timely evaluation and intervention can help lead to effective management.
The affected arm should generally be rested to facilitate the healing of the inflamed bursa. Complete immobilisation is not always required, and gentle movements or exercises may be conducted at the discretion of the elbow specialist to help maintain the range of motion and prevent stiffness.
Untreated elbow bursitis can lead to chronic pain and sustained swelling, potentially limiting the range of motion and overall functionality of the elbow. In cases of infectious bursitis, the risk of spreading infection increases. Timely consultation with an elbow specialist can help lead to appropriate treatment, especially in persistent or worsening cases.
Exercises like elbow flexion and extension, wrist movements using light weights or resistance bands, and forearm movements may assist in the management of elbow bursitis. Specific exercises should be discussed with the elbow specialist for personalised guidance that aligns with the individual’s condition and recovery goals.