Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
A stress fracture in the foot or ankle is a small crack in a bone, or in some cases, severe bruising within a bone. This condition typically affects the weight-bearing bones of the lower extremities, such as the second and third metatarsals in the foot, which are more vulnerable due to their thinner structure.
These types of fractures most commonly occur as a result of repetitive forces absorbed during activities like walking and running.
Stress fractures of the foot and ankle are predominantly caused by overuse and repetitive stress on the bones. Several factors contribute to the development of these fractures:
Stress fractures are characterised by several symptoms and signs, which can vary based on the location and extent of the fracture.
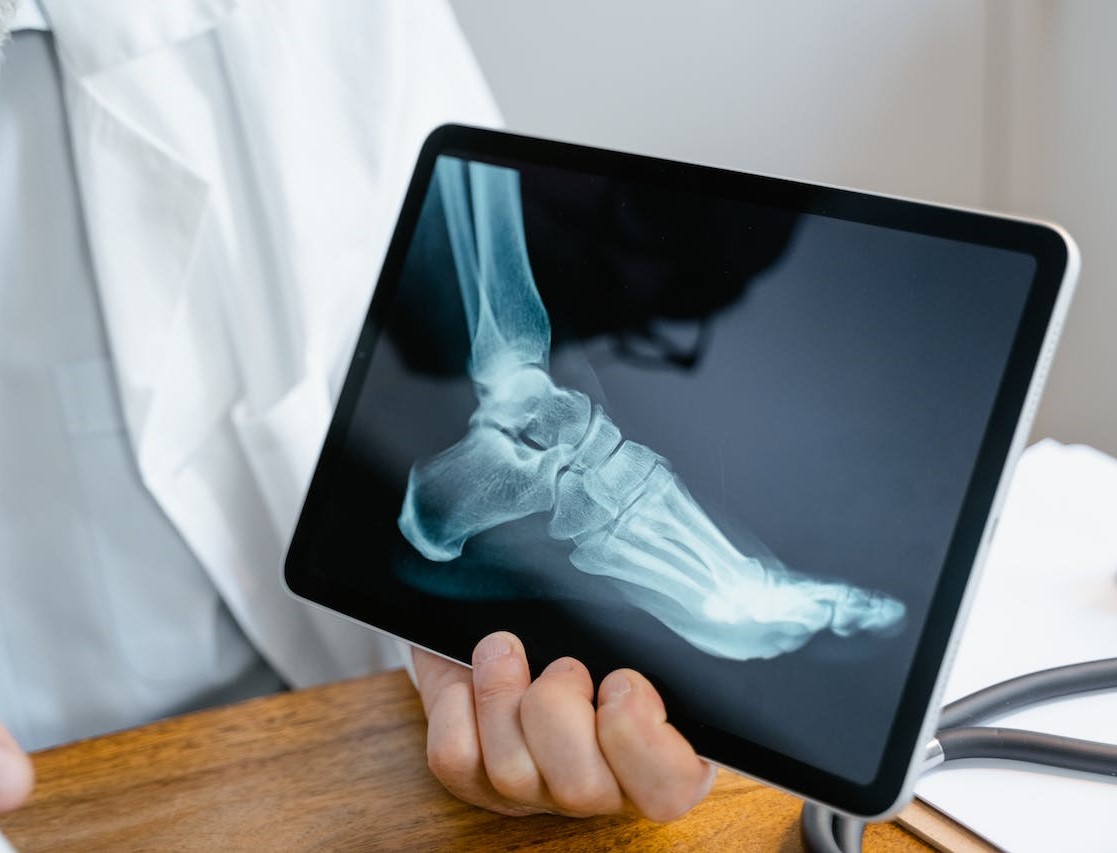
The diagnosis of stress fractures in the foot and ankle involves a thorough evaluation by a foot and ankle specialist.
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of approach for stress fractures of the foot and ankle. These aim to relieve pain, support the healing process, and prevent further injury.
Rest and Activity Modification |
Initially, the foot and ankle specialist may suggest reducing or ceasing activities that put weight on the affected area. This is intended to allow the bone time to heal. Activities that involve high impact or stress on the foot and ankle should also be avoided or reduced. |
Protective Footwear |
Wearing shoes that provide proper support and cushioning can help alleviate stress on the fracture site. In some cases, specialised footwear or orthotic devices may also be recommended. |
Crutches, Walking Boots, or Casting |
In more severe cases, these tools may be used to offload weight from the affected foot and ankle to aid in healing. |
Physical Therapy |
After a period of rest, physical therapy can help gradually rebuild strength and mobility in the foot and ankle. |
Anti-Inflammatory Medication |
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to manage pain and reduce swelling. These should be used with caution, as they occasionally impair bone healing. |
In cases where non-surgical treatments for stress fractures of the foot and ankle are insufficient, or if the fracture is severe, surgical intervention may be required.
This is a common surgical procedure for stress fractures that have not healed adequately with conservative treatment. It involves the use of surgical hardware such as pins, screws, or metal plates to secure the bones in the correct position, allowing them to heal properly.
In some instances, particularly when there is a large gap or poor bone quality, a bone graft may be necessary. This involves transplanting bone tissue to promote healing and provide structural support to the fractured bone.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Making lifestyle adjustments and being aware of risk factors may help in reducing the risk of stress fractures.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Engaging in exercise or weight-bearing activities with a stress fracture in the foot or ankle should be approached with caution. Continuing physical activity may exacerbate the injury, potentially leading to more severe fractures or prolonged recovery. Consult a foot and ankle specialist before resuming any physical activity, to explore options that work for your specific condition.
The healing time for a foot or ankle stress fracture varies depending on several factors, including the fracture’s severity, location, and the individual’s overall health. Typically, it can take from 6 to 8 weeks for a stress fracture to heal adequately.
Ignoring a stress fracture in the foot or ankle can lead to complications, such as the fracture becoming more severe or developing into a chronic condition. Early diagnosis and treatment may contribute to better healing outcomes and could help in preventing further damage.
Stress fractures differ from other types of fractures in that they are usually caused by overuse or repetitive activity, rather than a single traumatic event. They often appear as small cracks or severe bruising within a bone, particularly in weight-bearing bones of the foot and ankle. Unlike acute fractures that result from a specific injury, stress fractures develop gradually and are often associated with increasing levels of physical activity or changes in exercise routines.