Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
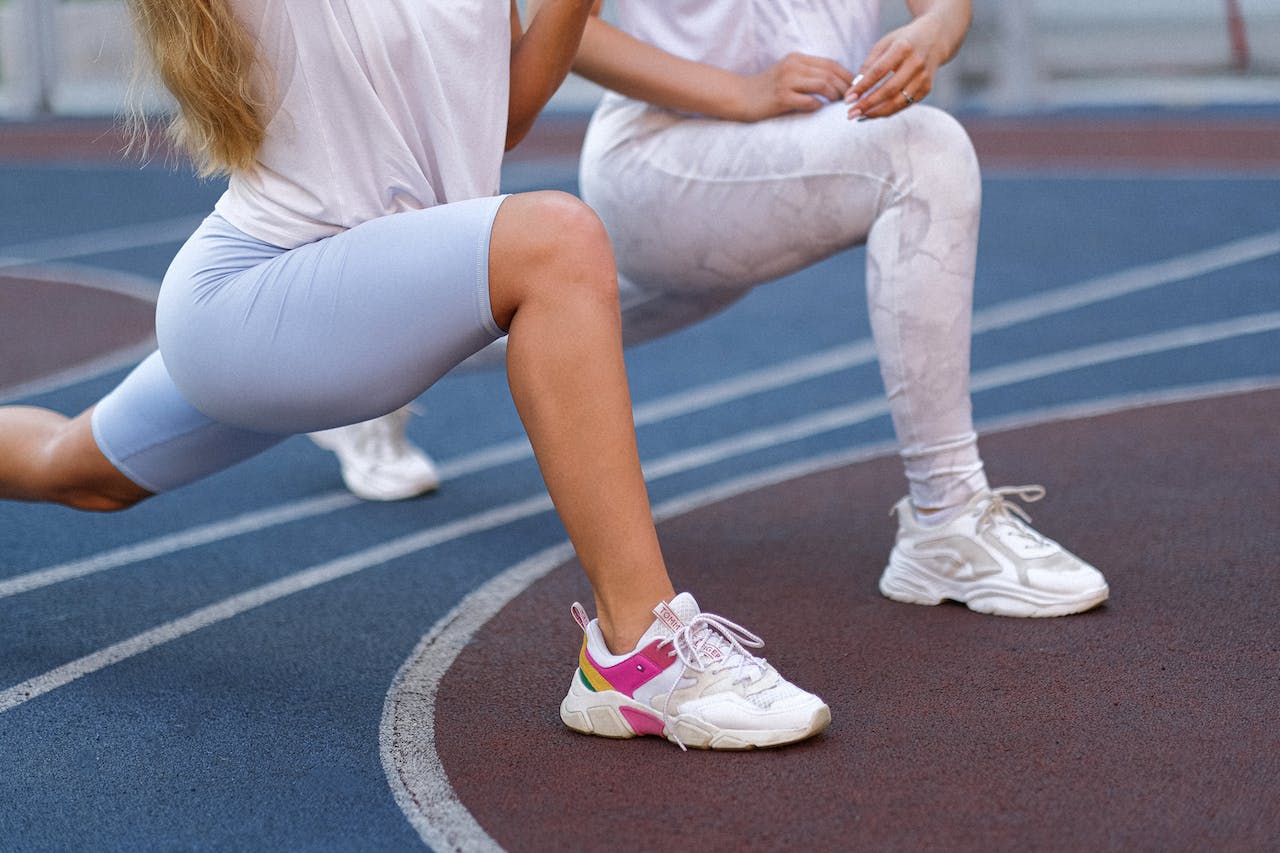

Hamstring muscle injuries encompass a range of conditions affecting the hamstring muscles. These muscles, namely the semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and biceps femoris, are located at the back of the thigh. Their primary function is to facilitate the bending of the knee. Injuries to the hamstring muscles are common among athletes engaged in activities that demand sprinting and jumping, such as track, soccer, and basketball.
The severity of hamstring muscle strains can be classified into three grades. Grade 1 strains are mild and typically heal readily. Grade 2 strains involve more extensive damage. While the muscle is not completely ruptured, there are a greater number of muscle fibres being affected. Grade 3 strains are the most severe, characterised by a complete tear of the muscle, which may require months to heal.
Hamstring muscle injuries often result from a combination of factors. The primary cause is muscle overload, where the muscle is either stretched beyond its capacity or subjected to a sudden, substantial load. Various factors can contribute to the risk of hamstring injuries:
Individuals with a strained hamstring typically experience:
The process of diagnosing a hamstring muscle injury involves several steps:
The approach to treating hamstring muscle injuries largely depends on the injury's nature and severity. Non-surgical treatments, which are typically effective for most hamstring injuries, include the following.
RICE Therapy and Activity Modification |
Initially, the orthopaedic specialist may suggest using rest, ice, compression, and elevation to help reduce pain and swelling. Activities that aggravate the injury can also be avoided or modified to help the muscles heal without further stress. |
Physical Therapy |
The orthopaedic specialist may also recommend engaging in physical therapy. This can stretch the injured muscle and scar tissue to maintain flexibility and help restore muscle strength. |
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections |
For higher-grade tears, platelet-rich plasma injections may be considered to support the healing process. |
Surgery is generally considered when non-surgical treatments fail to yield results, especially in grade 3 tears. Active individuals or athletes who have completely torn their hamstring muscle from the pelvis or shinbone are primary candidates for surgical repair.
During the procedure, the torn muscle is reattached to the bone. In cases of severe muscle tears, a surgical repair can be employed to restore the normal anatomy and function of the hamstring muscles.
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
The risk of developing hamstring muscle injuries can be reduced by several proactive measures:

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
The healing time for a hamstring muscle injury varies with its severity. Grade 1 and 2 strains may heal between 3-8 weeks, while grade 3 tears, involving a complete muscle tear, may require several months, particularly if surgical repair is needed.
Quick recovery from a hamstring injury involves adhering to prescribed treatment plans, which may include RICE therapy and physical therapy. For effective recovery, follow the treatment plan recommended by your orthopaedic specialist.
Walking capability depends on the injury’s severity. Minor strains might allow for gentle walking, but more severe injuries could limit this ability. Our orthopaedic specialist can guide you through strategies that can help improve your mobility and prevent aggravation of the injury.
Avoid activities that cause pain, swelling, or discomfort in the injured area. This includes high-impact exercises, heavy lifting, and sudden movements that could strain the hamstring further. Consulting with an orthopaedic specialist can offer specific guidance based on your injury’s nature and severity.