Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
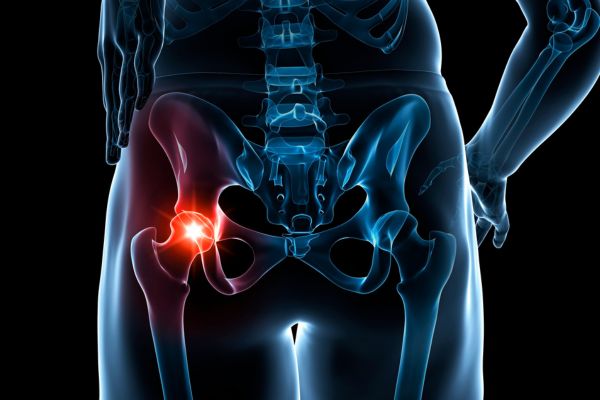
A hip labral tear is a condition characterised by damage to the labrum, a fibrous ring of tissue surrounding the socket part of the hip joint (acetabulum). The hip joint itself is a ball-and-socket joint, where the rounded head of the femur (thighbone) fits into the acetabulum of the pelvis. The labrum acts like a rubber seal to maintain the position of the femoral head within the hip socket, ensuring smooth and stable movement. When a tear in the labrum occurs, it can compromise the integrity of the hip joint, leading to discomfort and impaired mobility.
This type of injury disrupts the normal function of the labrum, leading to issues such as pain, limited range of motion, and sensations of clicking or locking in the hip joint.
Hip labral tears can result from a variety of factors, each contributing to the weakening or damage of the labrum:
Individuals with a hip labral tear may experience a range of symptoms, which can vary in intensity and frequency:
The process of diagnosing a hip labral tear involves several steps to accurately identify the condition and assess the extent of the injury.
Medical History Review |
Initially, the hip specialist will inquire about the patient’s medical history, including any previous hip injuries, sports participation, and the onset and nature of the current symptoms. |
Physical Examination |
A hip specialist will conduct a thorough physical examination. This includes checking the range of motion in the hip, assessing for any pain or discomfort during movement, and performing specific tests to provoke symptoms related to a labral tear. |
Imaging Tests |
MRI scans are often used to confirm a hip labral tear. It can reveal the presence and extent of a tear. While X-rays or CT scans cannot show soft tissue like the labrum, they may be used to identify any associated bony deformities in the hip. |
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of approach for hip labral tears, especially in cases where the tear is not extensive or the patient has specific reasons to avoid surgery. These focus on alleviating symptoms and improving hip function.
When non-surgical treatments are not effective in alleviating the symptoms of a hip labral tear, surgical options may be considered. Many hip labral tears are treated using hip arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure which can aid the repair or removal of the damaged labrum with smaller incisions and greater accuracy.
Depending on the nature and severity of the tear, the hip surgeon may either repair the torn labrum by sewing it back together or remove the torn portion. The decision is based on factors such as the quality of the labral tissue and the overall stability of the hip joint.
During the procedure, bony deformities of the acetabulum (socket) and femoral head and neck (ball) which are associated with the tear can also be addressed. This could involve reshaping the bones to prevent future impingement and tearing.
While not all hip labral tears can be prevented, especially those due to structural abnormalities or degenerative changes, measures can be taken to help reduce their risk.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Recovery time from a hip labral tear varies depending on the treatment approach. For non-surgical treatments like medication and physical therapy, recovery can take 8 to 12 weeks. If surgery is necessary, the timeline extends, with low-intensity exercise possible in about three months and a return to regular routines potentially taking more than four months.
Leaving a hip labral tear untreated can lead to chronic pain and instability in the hip, potentially causing further damage. These conditions may require more intensive treatments, including surgical intervention, in the future. Consult our hip specialist to explore treatment options and prevent the progression of the condition.
Hip labral tears typically do not heal on their own and require intervention for improvement. Continuing regular activities without treatment may worsen the condition, leading to more severe injuries. Early consultation with our hip specialist can help lead to appropriate management and treatment.
Walking with a hip labral tear is possible, but it may cause pain or discomfort, especially during extended periods of activity. Consult our hip specialist for an individual assessment and guidance on activity levels.
The best exercises for a hip labral tear focus on strengthening the muscles around the hip and improving flexibility. This includes activities that enhance hip and core strength, stability, and range of motion. Exercises should be tailored to individual needs to avoid exacerbating the condition.