Schedule An Appointment With Us
Are Your Symptoms Affecting Your Quality Of Life?
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
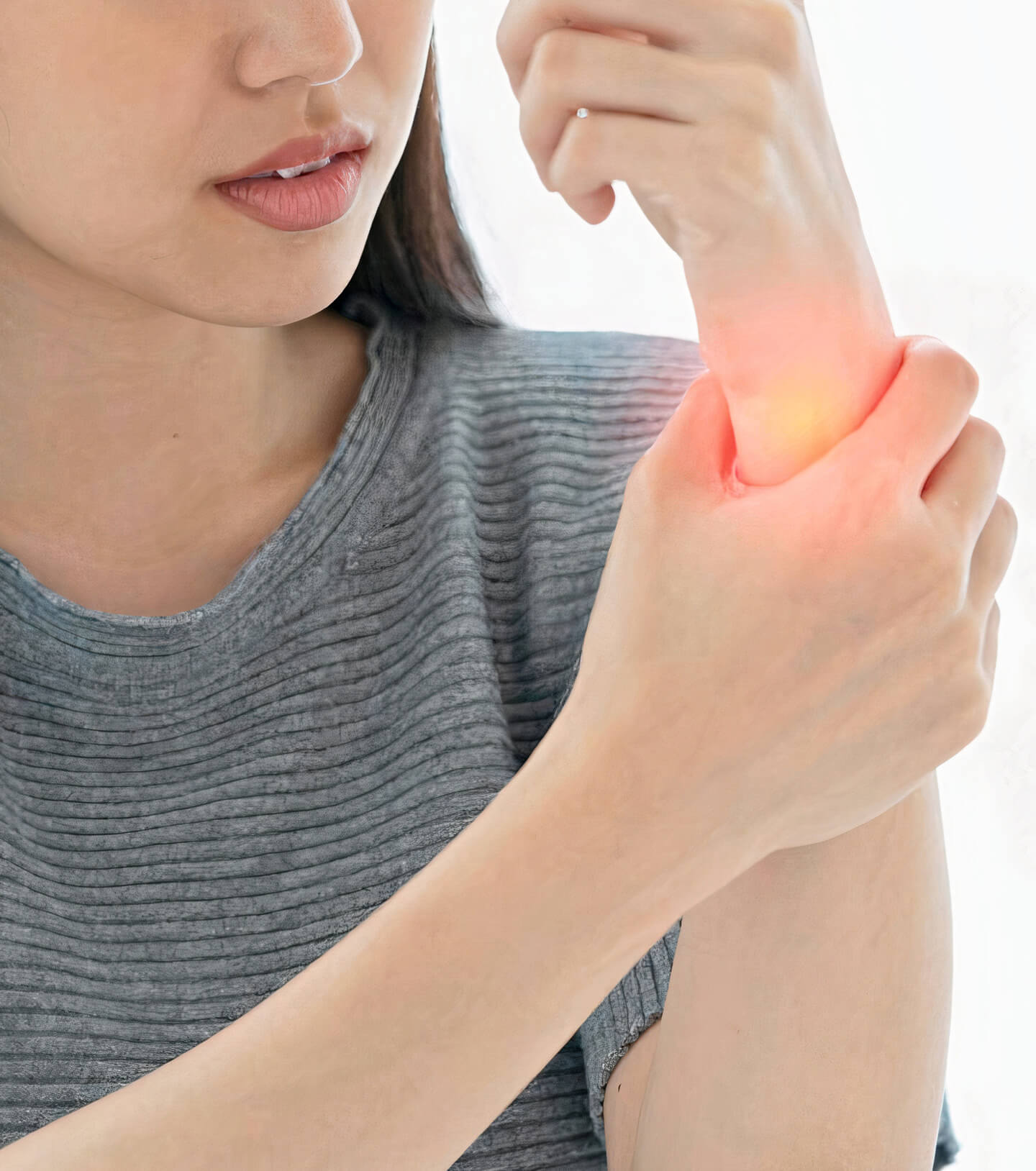
Wrist arthritis is a condition characterised by inflammation and degeneration of the joints within the wrist. It leads to the deterioration of the cartilage, the smooth covering at the ends of bones where they form a joint. As cartilage wears away, bones may rub against each other, causing pain and limiting movement. Since the wrist is necessary for hand movements and dexterity, wrist arthritis can impact daily activities.
Wrist arthritis can manifest in several forms, each with unique characteristics.
Often related to age, osteoarthritis occurs due to the wear and tear of cartilage over time. It is common in individuals over the age of 50.
This is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, including the joints. It can affect the wrist joints and often involves both wrists.
This type develops following an injury to the wrist, such as a fracture or sprain, which may damage the cartilage and lead to arthritis over time.
Associated with the skin condition psoriasis, this type can affect the wrist and cause joint inflammation.
This is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joint. It is a painful form of arthritis that can occasionally affect the wrist.
The symptoms of wrist arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Several factors can influence the development of wrist arthritis:
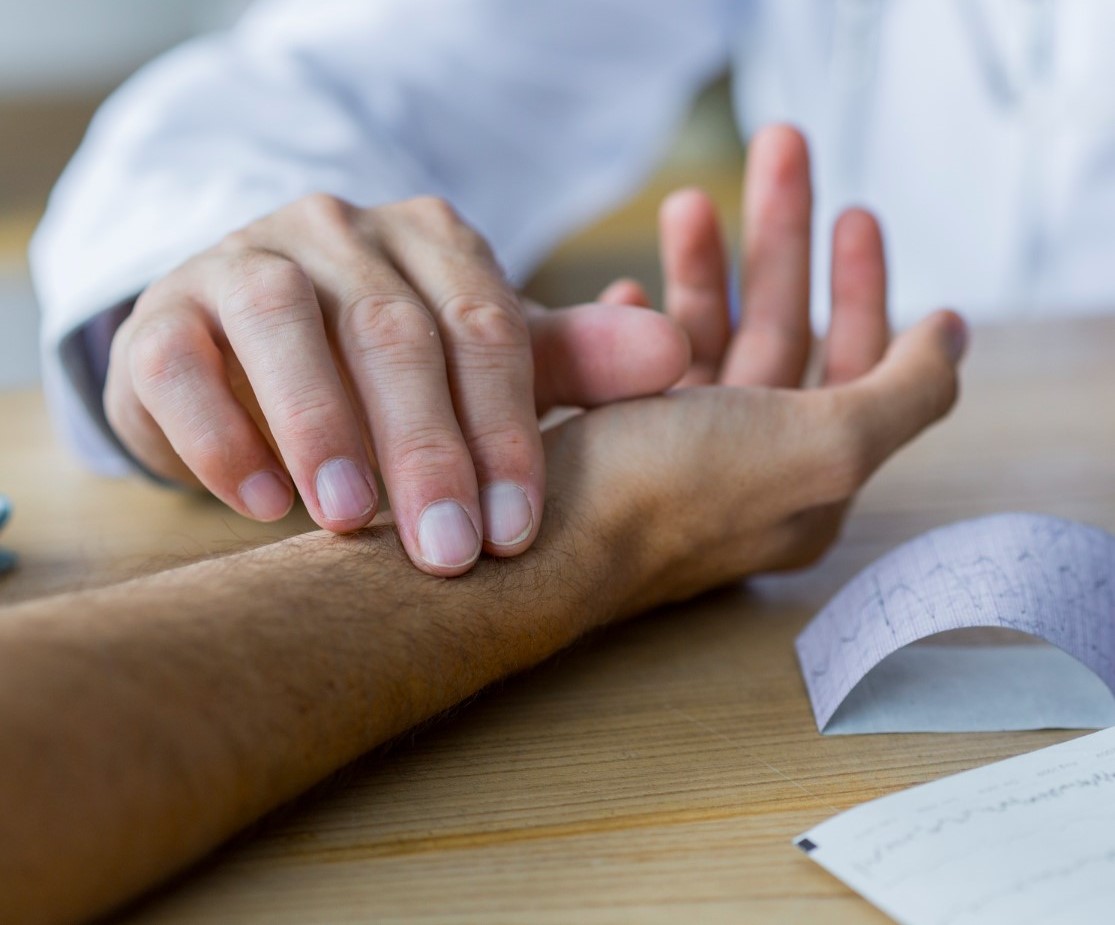

Diagnosing wrist arthritis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests.
Non-surgical treatments for wrist arthritis focus on relieving symptoms and improving joint function.
Wearing a wrist splint or brace can stabilise the joint, alleviate pain, and prevent further damage, especially during activities.
A tailored exercise program can strengthen the muscles around the wrist, improve range of motion, and reduce stiffness. Physical therapists may also employ techniques like heat or cold therapy and ultrasound.
Helps patients learn new ways to accomplish daily tasks with less pain and stress on the joints.
When non-surgical treatments are insufficient in managing symptoms or when wrist arthritis is particularly severe, surgical options may be considered.
Arthroscopic Debridement |
A minimally invasive surgery where small incisions are made, and a camera (arthroscope) is inserted into the wrist joint. The surgeon can clean the joint area, removing loose cartilage, inflamed tissue, or bone spurs. |
Joint Fusion (Arthrodesis) |
In this procedure, the bones of the joint are fused. It provides pain relief but may reduce mobility of the wrist. It’s often considered for severe arthritis where motion is already limited. |
Total Wrist Arthroplasty (Wrist Replacement) |
This involves replacing the affected joint with artificial components. Wrist replacement can relieve pain and preserve more wrist motion than fusion, but it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with high physical demands. |
Proximal Row Carpectomy |
This surgery involves removing some of the carpal bones from the wrist, which can relieve pain while maintaining some level of wrist motion. |
Denervation |
This involves cutting the nerves around the arthritic joint to alleviate pain. It does not address the underlying arthritis. |
Schedule An Appointment With Us
Consult our MOH-accredited orthopaedic surgeon for an accurate diagnosis & personalised treatment plan.
While it’s not always possible to prevent wrist arthritis, certain strategies can reduce the risk and possibly slow the progression of the disease.

MBBS
MRCSEd
MMED (Ortho)
FRCSEd
With over 20 years of experience, Dr Poh Seng Yew is an orthopaedic surgeon specialising in hip, knee, shoulder and elbow surgery, sports medicine, and trauma surgery.




Weekdays: 9.00am – 5.00pm
Saturdays: 9.00am – 1.00pm
Sundays and Public Holidays: Closed
Please leave us a message, and we will be in touch with you shortly.
Early signs include joint stiffness, particularly in the morning, mild pain during activities, and occasional swelling in the wrist.
While there is no cure for arthritis, the symptoms can be managed effectively through various treatments and lifestyle changes.
Wrist arthritis typically causes pain and stiffness in the wrist joint, whereas carpal tunnel syndrome causes numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand. A medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help reduce inflammation and joint pain.
Severe, untreated wrist arthritis can lead to pain and loss of function, potentially impacting daily activities. Early treatment can help prevent disability.
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and individual factors, but it generally ranges from several weeks to several months.